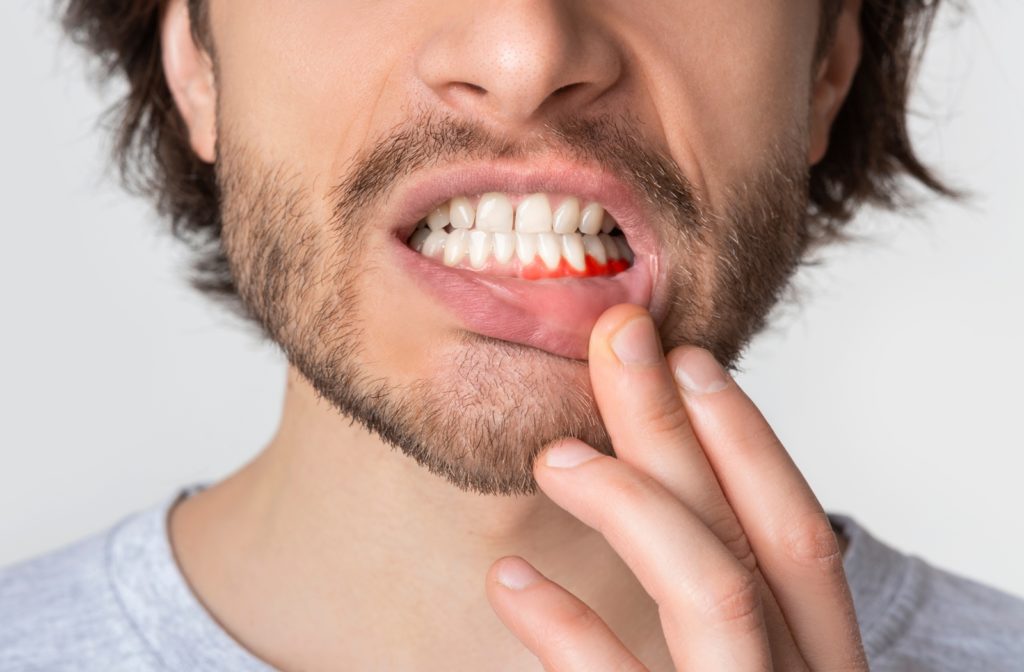
Infected gums, also known as gum disease or periodontal disease, can be painful and uncomfortable to deal with. Unless you have visited for a dental exam recently, you may not be sure if you’re suffering from infected gums. If left untreated, these infections can develop into serious diseases.
If you’ve been dealing with the symptoms below, we strongly recommend you visit a dentist to discuss treatment options.
Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of gum infections early is key. If your gums are healthy, they should be firm and pale pink in colour. As well, your gums should feel like they fit firmly around your teeth.
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms below, even mildly, visit your dentist to receive the proper management and treatment.
Gum Recession
Healthy gums should fit snugly around your teeth. Gum recession is the process of gum tissue wearing away or pulling back. If this happens, gaps are created between your teeth and gums, leaving an open area for bacteria to collect.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums should not be a common occurrence in oral health. However, they don’t immediately mean you’re suffering from a gum infection. Before you think it’s a gum infection, make sure you aren’t doing the following:
- Brushing to hard
- Just starting a flossing routine
- Have poorly fitting dentures
- Suffering from faulty dental restorations
Red or Swollen Gums
In most cases, your gums should be a pale pink colour. If your gums have turned an irregular red or have increased in size, a gum infection may be the culprit. However, your gums may have changed in colour or size, similar to the same reasons as bleeding gums. If this is not the case, book a dental exam.
Toothaches
While there are many causes for toothaches, they can be an identifier of infected gums. Patients with toothaches may experience swelling, pain, or throbbing feelings around their teeth. As well, they may come down with a fever or a headache.
Gum Disease
If you’re experiencing the symptoms above, you may be dealing with one of the gum diseases below. While these diseases might start small, they can have serious effects on your oral health if not treated and managed properly.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, normally caused by a bacterial infection. This bacterial infection occurs in a small space where teeth and gums connect. Every time we eat or drink, bacteria can get trapped in this space. If not cleaned away, the bacteria will become plaque, eventually turning into tartar.
If plaque continues to be left unremoved, the gums can begin to separate from the teeth. This separation is an early sign of periodontitis and could mean tooth loss or removal if not dealt with in a timely fashion.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can develop into periodontitis. This disease can have more serious effects on your oral health. As the gums continue to separate from the teeth, the bone support will also begin to loosen. The deterioration of these structures can cause patients pain and bleeding when chewing. If left untreated, severe periodontitis can mean tooth loss or removal for some patients.
If you’re interested in learning more about gum disease or are concerned about your oral health, book an appointment for a dental exam.

Risk Factors
While gum disease is often largely connected to oral hygiene, other risk factors can increase your chances of developing gum diseases. It’s important to be aware of these risk factors so the proper prevention methods can be used.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Diabetes
- Certain medications such as steroids, anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, and chemotherapy
- Crooked or misaligned teeth
- Poorly fit dental appliances
- Broken fillings
- Pregnancy
- Genetic factors
- Compromised immunity systems
Treatment & Prevention
Whether you are at risk or have been diagnosed with gum disease, it’s important to be aware of the prevention and treatment methods available to you.
Treatment
If gum disease has developed, multiple treatments can be used to reduce pain and the effects of the disease. However, it’s important to first visit your dentist to see what treatment methods they recommend.
Common gum disease treatment methods include:
- Antibiotic therapy
- Root planing and scaling treatment
- Gingivectomy
- Flap surgery
Prevention
Preventing gum disease starts with following proper oral care habits. These include brushing twice a day and flossing at least once a day. In addition to these regular everyday activities, you can also use an anti-gingivitis mouthwash to kill bacteria that wasn’t cleaned away from brushing or flossing. These preventative steps can help protect your gums from disease, as well as promote healthier oral hygiene.
Outside of your regular at-home care, regular dental exams and cleanings are important in removing any plaque that has built up on your teeth. We recommend an exam and cleaning once every 6 months.
When to See a Dentist
If you’re suffering from the symptoms above, it’s best to book an appointment with a dentist to identify if there are serious issues that could lead to infected gums. If these issues are dealt with early, more treatment options are available and you could avoid a less uncomfortable and expensive procedure. Interested in learning more about your gums and oral health? Come in for a visit!